Part3
Maximum path sum
❓: A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node's values in the path.
Example:
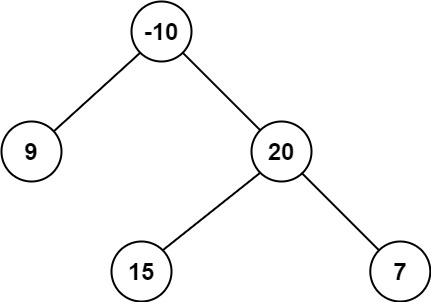
Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 42
Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.res = root.val
self.helper(root)
return self.res
def helper(self, node):
if not node:
return 0
ls = max(0, self.helper(node.left))
rs = max(0, self.helper(node.right))
self.res = max(self.res, node.val + ls + rs)
return node.val + max(ls, rs)
var res int
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
res = root.Val
helper(root)
return res
}
func helper(node *TreeNode) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
l := max(0, helper(node.Left))
r := max(0, helper(node.Right))
res = max(res, node.Val+l+r)
return node.Val + max(l, r)
}
Construct Binary Tree from inorder and preorder
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not preorder:
return
root_val = preorder.pop(0)
node = TreeNode(root_val)
root_inorder_ind = inorder.index(root_val)
node.left = self.buildTree(
preorder[:root_inorder_ind], inorder[:root_inorder_ind]
)
node.right = self.buildTree(
preorder[root_inorder_ind:], inorder[root_inorder_ind + 1 :]
)
return node
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(preorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
root_val := preorder[0]
preorder = preorder[1:]
root_inorder_ind := slices.Index(inorder, root_val)
root := TreeNode{Val: root_val}
root.Left = buildTree(preorder[:root_inorder_ind], inorder[:root_inorder_ind])
root.Right = buildTree(preorder[root_inorder_ind:], inorder[root_inorder_ind+1:])
return &root
}
Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not postorder:
return
root_val = postorder.pop()
node = TreeNode(root_val)
root_inorder_ind = inorder.index(root_val)
node.left = self.buildTree(
inorder[:root_inorder_ind], postorder[:root_inorder_ind]
)
node.right = self.buildTree(
inorder[root_inorder_ind + 1 :], postorder[root_inorder_ind:]
)
return node
func buildTree(inorder []int, postorder []int) *TreeNode {
if len(postorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
root_val := postorder[len(postorder)-1]
postorder = postorder[:len(postorder)-1]
root_inorder_ind := slices.Index(inorder, root_val)
root := TreeNode{Val: root_val}
root.Left = buildTree(inorder[:root_inorder_ind], postorder[:root_inorder_ind])
root.Right = buildTree(inorder[root_inorder_ind+1:], postorder[root_inorder_ind:])
return &root
}
Symmetric Binary Tree
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
return self.helper(root.left, root.right)
def helper(self, left_node, right_node):
if left_node is None:
return right_node is None
if right_node is None:
return left_node is None
return (
left_node.val == right_node.val
and self.helper(left_node.left, right_node.right)
and self.helper(left_node.right, right_node.left)
)
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
return helper(root.Left, root.Right)
}
func helper(left *TreeNode, right *TreeNode) bool {
if left == nil {
return right == nil
}
if right == nil {
return left == nil
}
return left.Val == right.Val && helper(left.Left, right.Right) && helper(left.Right, right.Left)
}
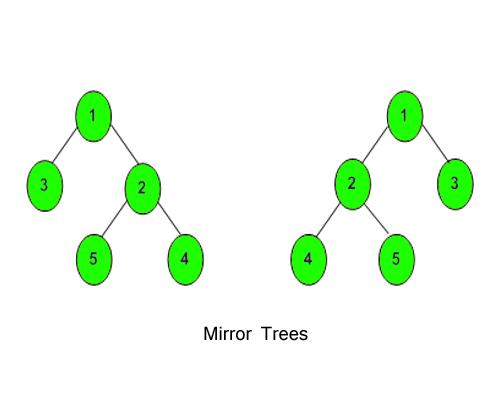
Mirror Tree
Given a Binary Tree, convert it into its mirror.
class Solution:
def mirror(self, root):
if not root:
return
root.left, root.right = root.right, root.left
self.mirror(root.left)
self.mirror(root.right)
Check for Children Sum Property
❓: Given a binary tree having n nodes. Check whether all of its nodes have a value equal to the sum of their child nodes. Return 1 if all the nodes in the tree satisfy the given properties, else it returns 0. For every node, the data value must be equal to the sum of the data values in the left and right children. Consider the data value 0 for a NULL child. Also, leaves are considered to follow the property.
Example:
35
/ \
20 15
/ \ / \
15 5 10 5
Explanation: Here, every node is sum of its left and right child.
class Solution:
def isSumProperty(self, root):
if not root:
return 1
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return 1
left = root.left.data if root.left else 0
right = root.right.data if root.right else 0
return (
(1 if root.data == left + right else 0)
and self.isSumProperty(root.left)
and self.isSumProperty(root.right)
)